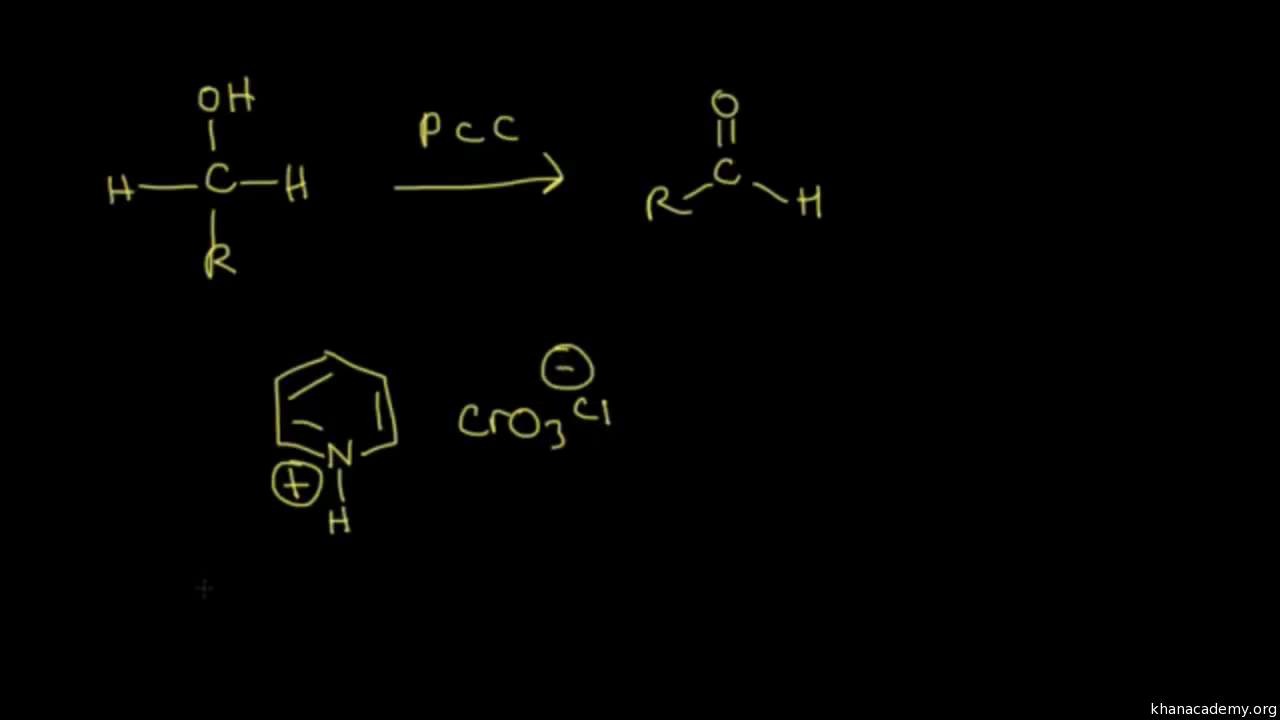
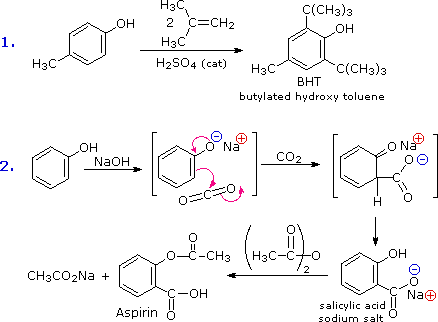
Need to Know Reactions Exam 03 You should be able to answer questions about the following reaction types on exam 3 Oxidations R OH PCC R O H 1) O3 2) Zn, AcOH O H O CrO3 H3O R H O R OH O Jones Oxidation OH O CH3 KMnO4 OH O KMnO4 2 OH O OH CrO3 H3O OH O KMnO4 2 O Reductions (Hydrides, Grignards and Gilman Reagents)Good place to work Laborer/Operator (Current Employee) Crooksville, OH Good supervisors, employees help each other, standing for 12 hours is the hardest part PCC Airfoils is the world leader in Investment Castings PCC Airfoils produces components, which are extremely close tolerances required by the manufactures of today'sPyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a yelloworange salt with the formula C 5 H 5 NH CrO 3 Cl −It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonylsA variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity PCC offers the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, whereas many other reagents are less
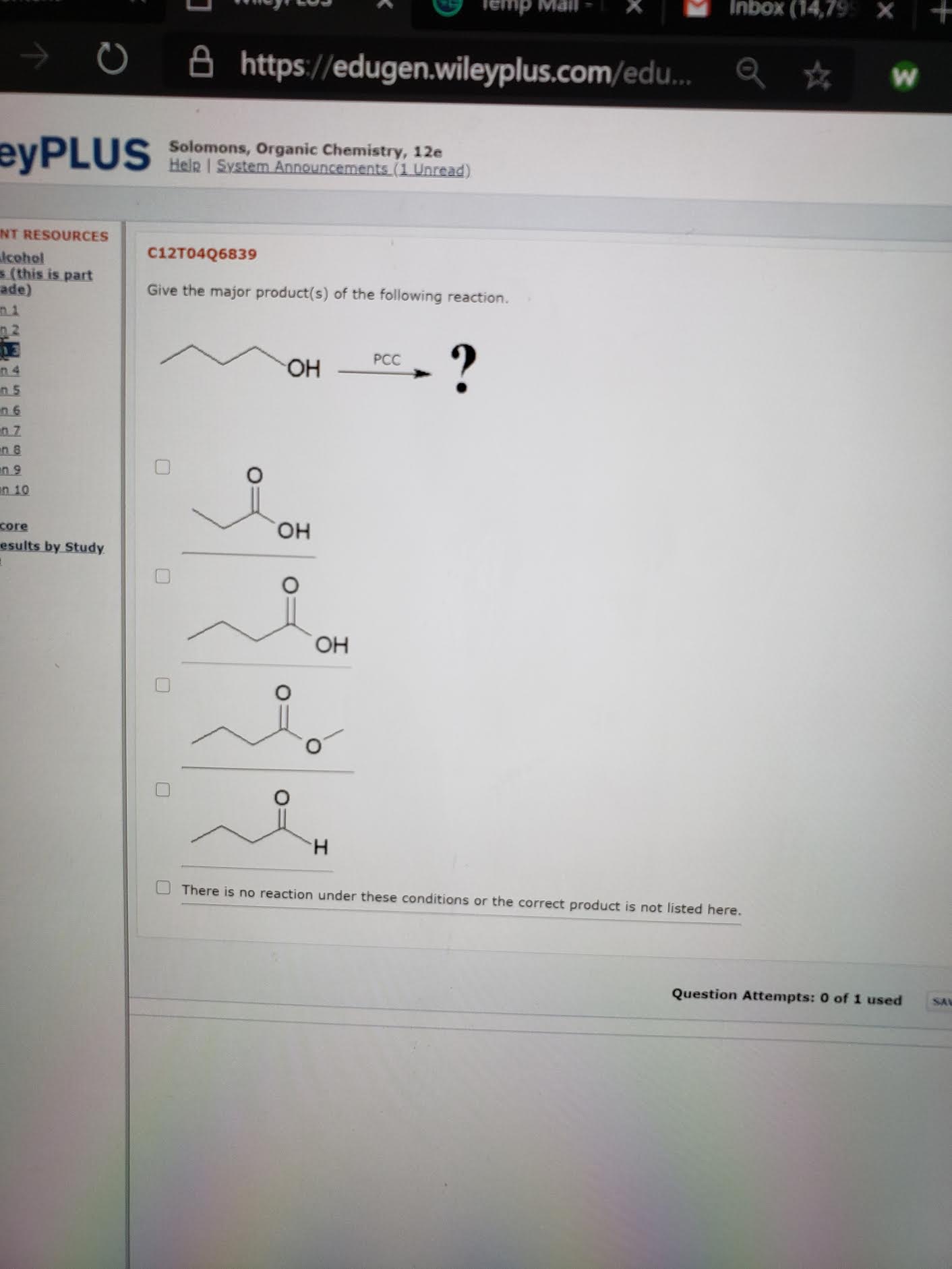
Answered Give The Major Product S Of The Bartleby
Oh pcc reaction
Oh pcc reaction-To make alcohols more nucleophilic, need to abstract the acidic hydrogen!OH oxone NaBr CH,CN, H2O OH OH H III IV A) B) II C) III D) IV 29 Determine the product of the following reaction OH PCC (excess) OH CH2Cl2 & OH IV A) B) 11 11 C) III D) IV Question 28



Alcohol Reactivity
Start studying Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsReactions of Ethers 1 Ethers do not react with oxidizing or reducing agents 2 Combustion ether oxygen carbon dioxide water CH3OCH3 3 O2 2 CO2 3 H2O 3 Reaction with Concentrated Binary Acids 4 Reaction with Atmospheric Oxygen • This is a slow reaction in which highly unstable peroxides are formedScience Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Determine the product of the followin OH PCC (excess) "OH CH,C12 ono van & mi in "OH INI IV
OH Jones (CrO3, H) or PCC R1 R2 O R1 OH R1 O OH Jones (CrO3, H) R1 OH R1 O H PCC Williamson Ether Synthesis R1 R2 OH R1 R2 O NaH Na CH3I R1 R2 O CH3 Ether Cleavage Reactions R1 R2 OH HI CH3I R1 R2 O CH3 R O CF 3CO2H R OH Chem 342 page 2 Spring 09 Epoxide Formation CH 3 CH 3 O MCPBA CH 3 OH Br Br2, H2O NaH Epoxide OpeningThe present invention relates to a process of preparing precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) in a low energy intensity reactor in such a manner that the amount of solids in the PCC product can be raised to 35% or more without performing a dewatering step The process comprises performing in parallel and in two or more separate reaction vessel the steps of contacting calcium hydroxideOH OH O A) KMnO 4 /NaOH/H 2 O O Topic Reactions of Alcohols Section 1310 Difficulty Level Medium 1 140 1 Predict the product for the following reaction PCC cis 4methylcyclohexanol CH 2 Cl 2 Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 /H 2 SO 4 /H 2 O O O
NUC H H H OH Usually the hydroxide, or alkoxide, is a BAD leaving group,!Reaction with Ketones or Aldehydes (Section 1816,17 and 1910) R' R O aldehyde or ketone ZNH 2, H R' NHZ OH R tetrahedral "aminol" , O H2O, H, ZNH2 H 2O, H imine R' R NZ Notes • "Z" can be a carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, or hydrogen atom/group • The "aminol" can't be isolated, it's only present at equilibriumAlcohol Reactions The functional group of the alcohols is the hydroxyl group, –OHUnlike the alkyl halides, this group has two reactive covalent bonds, the C–O bond and the O–H bond The electronegativity of oxygen is substantially greater than that of carbon and hydrogen



Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc




4 H2o 5 Pcc Ch2cl2 Hno3 A Ca Oh 2 Organic Chemistry
Chemistry questions and answers 28 What is the product of the following reaction?MiniEncyclopedia of Papermaking WetEnd Chemistry Additives and Ingredients, their Composition, Functions, Strategies for Use PRECIPITATED CALCIUM CARBONATE (PCC) Composition Most PCC added to the wet end of paper machines consists almost entirely of the calcite crystal form of CaCO3The calcite crystal can have several different macroscopic shapesPropanol and PCC reaction When propanol is oxidized by PCC, propanal (an aldehyde compound) is given as the product CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH PCC → CH 3 CH 2 CHO How oxidation numbers are changed in oxidation of propanol?




Determine The Product Of The Following Reaction Pcc Excess Oh Ch2cl2 Oh Oh Oni On Homeworklib




Consider The Reaction Below Oh Pcc O Cr C Organic Chemistry
In propanol, the carbonol carbon atom's oxidation number is 1 With PCC, propanol gives propanalThe decomposition of 1º and 2ºalkyl hypochlorites, referred to earlier, is an example of such a reaction RCH 2 –OH hot Cu RCH=O H 2 RCH 2 –O– Cl base RCH=O H– Cl The most generally useful reagents for oxidizing 1º and 2ºalcohols are chromic acid derivatives Two such oxidants are Jones reagent (a solution of sodiumThe reaction given would give an aldehyde This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction Oxidation of a primary alcohol as in the reaction given by PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) in (dichloromethane) solvent yields an aldehyde Like chromic acid, PCC oxidizes alcohols




Answered Give The Major Product S Of The Bartleby



1
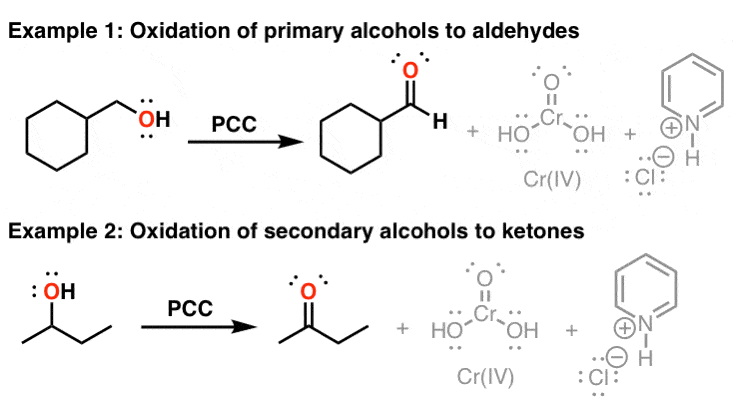
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a readily available, stable reagent, that oxidizes a wide variety of alcohols to carbonyl compounds with high efficiency E J Corey, J W Suggs, Tetrahedron Lett, 1975, 16, A domino oxidation of primary alcohols gives α,βunsaturated compounds using the combination of PCCNaOAc and stabilized Wittig Oxidation H 1 alcohol R C OH Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) H CH2Cl2, 25oC RC=O H 1o alcohol aldehyde H R C OH Cu or Cr3O/pyridine H RC=O H o 1 alcohol Cr3O/pyridine = Collins reagent aldehyde H R C OH H o 1 alcohol KMnO4/H orCan you write the reaction and electronpushing (arrowpushing) mechanism



Solved Determine The Product Of The Following Reaction Course Hero




Oxidations Pdf Chromium Alcohol
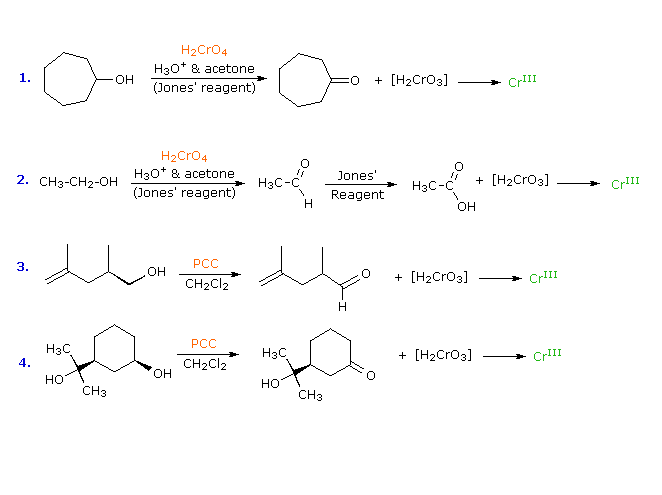
PCC is used in aprotic solvents, usually, dichloromethane As no water is present in the reaction mixture, no aldehyde hydrate is formed which is oxidized to carboxylic acid in presence of Cr(VI) OH H O PCC, DCM Geraniol Geranial OH H O PCC, dry CHCl 3, anhy AcOH, rt, 1h 1Teristics of the resulting PCC Ca(OH) 2(aq) CO (g) Þ CaCO 3 H O 31 Effects on Conductivity and pH Reactant concentration at a particular time during the course of the reaction can be monitored by conductivity and pH During the course of precipitation, the pH, conductivity (Fig 2) and TDS values gradually decreases in tandem with theOH C H3CH2 CH 3 H PCC or CrO3/H 2butanol 2 C 2butanone C OH CH3CH2 CH3 CH3 2methyl2butanol PCC or CrO3/H No reaction Figure 4 Oxidation reactions Summary of Figure 4 Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a mild oxidizing agent and chromic acid (CrO 3/H ) is a strong oxidizing agent Mild oxidizing agents can oxidize oxidizable carbon



Ochem




60 The Major Product Formed In The Following Reaction Is Pcc Pyridinium Chlorochromate Chci Ococh Ho
Expert Answer Who are the experts?1Substitution reaction of alcohols with HX ROH HX RX H 2O Works better with more substituted alcohols S N1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate rearrangements, stereochemistry (racemization) C H H R R H R C R C OH HROH H H HOH< < < increasing reactivity Mhl P rim ay (1 ¡)Se cond2Tt 3The oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids is an important oxidation reaction in organic chemistry When a primary alcohol is converted to a carboxylic acid, the terminal carbon atom increases its oxidation state by four Oxidants able to perform this operation in complex organic molecules, featuring other oxidationsensitive functional groups, must possess substantial




Organic Chemistry Oxidation Jones Reagent And Pcc
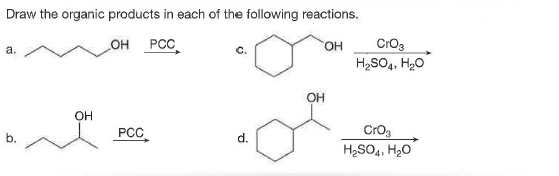



Answered Draw The Organic Products In Each Of Bartleby
PDC or PCC CrO3, H2SO4 Alcohols as Nucleophiles!Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ OH OH LOH 19 OH PCC (excess) ess), (A) 1 equivalent () CH3MgBrim NaBH4 H4>(D) H H2O Product (D) will be OH OH L CH – CH3 LOH (b) TOH OH OH OH c) I YOH OH (d)Therefore we need to convert the alcohol into a GOOD leaving group!



1




Ch17 C O Prep By Oxidation Of Roh
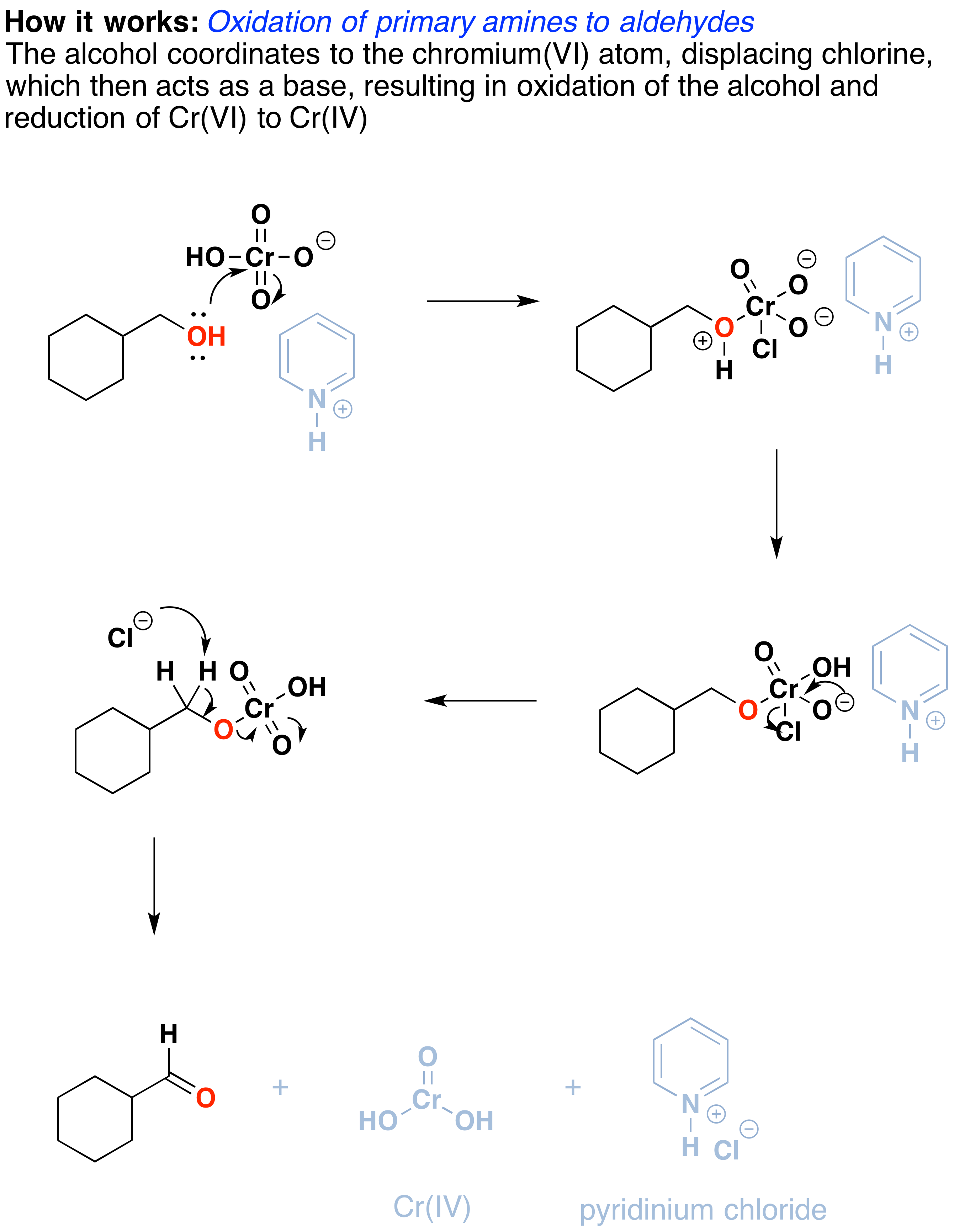
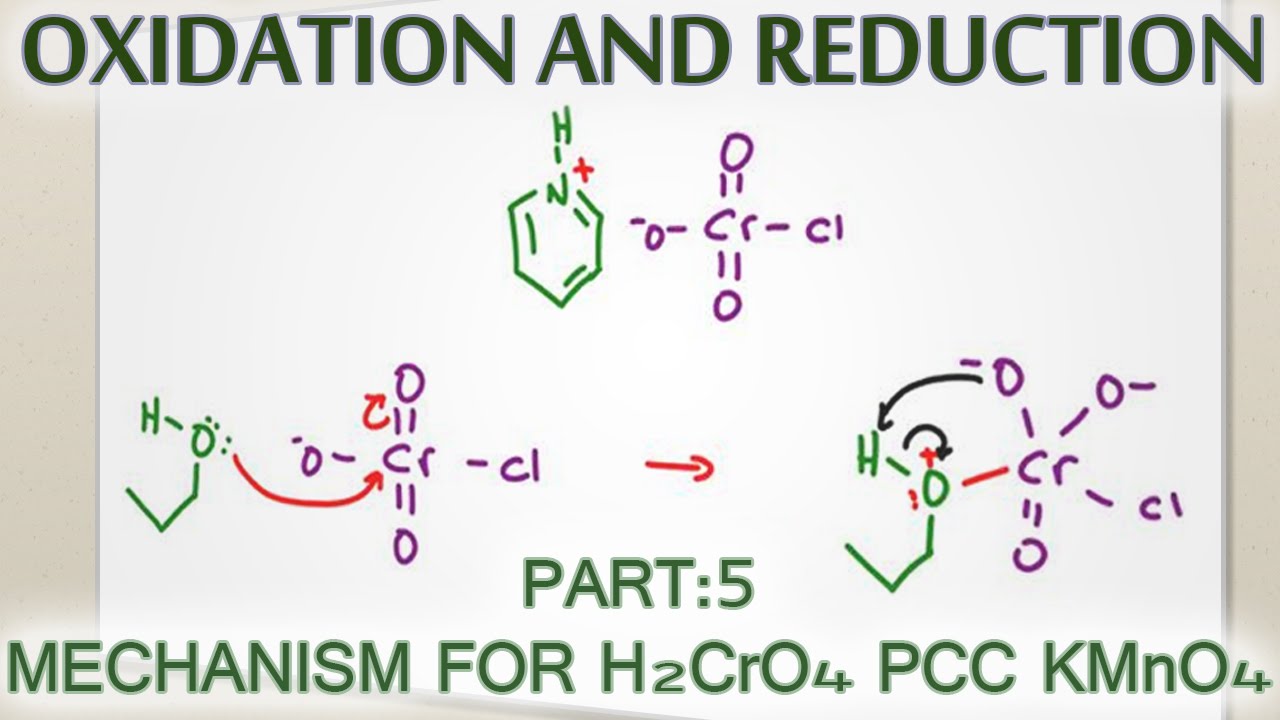
Oxidation of alcohols I Mechanism and oxidation states Oxidation of alcohols II Examples This is the currently selected item Biological redox reactions Protection of alcohols Preparation of mesylates and tosylates SN1 and SN2 reactions of alcohols Formation of nitrate esters Preparation of alkyl halides from alcoholsChlorochromate (PCC) use a similar mechanism O Cr O OH 2 H 2 SO 4 HO Cr OH O OH 2 O H 2 O HO Cr O O Cr OH O In the laboratory setting, there are a few different ways to prepare the Jones reagent One such method is to dissolve chromic trioxide in diluted sulfuric acid which forms chromic acid in situ The BeyondLabz platformFor the following reaction, select the statement that best describes the situation RCH_(2)OHPCCC_(5)H_(5)NH^()ClCrO_(3)^()rarrClass12Subject CHEMISTRY
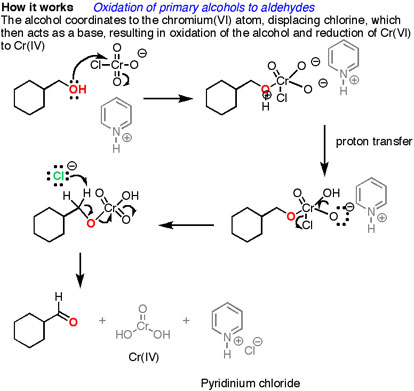



17 7 Oxidation Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts



Ochem
Can you write the reaction and electronpushing (arrowpushing) mechanism for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides?(the CO bond is broken during the reaction)!R OH R H PCC O Ch 16 9 OH O H PCC CH 2 Cl 2 (90%) PCC CH 2 Cl 2 OH O H (%) OH − No Reaction




Pcc Oxidation Mechanism Chemistry Steps




Oh Oh Loh 19 Oh Pcc Excess Ess A 1 Equivalent Ch3mgbrim Nabh4 H4 D H H2o Product D Will Be Oh Oh L Ch Ch3 Loh B Toh
A better leaving group), a nucleophilic substitution reaction can occur converting an oh Group into a Better Leaving Group One way to convert an OH group into a weaker base is to protonate it by adding acid to the reaction mixture Protonation changes the leaving group from HOto H PCC PCC, °, ° ° ° PCC PCC, °,OH C Ketone or Aldehyde Br 2 ∆ Cl 2 ∆ HBr Br 2 Br 2 H 2 O Br Cl Br O H Br HBr Br Br HBr Br Br Br Br Br Br Br 2 Br 2 Br Br Br Br HBr Br H 2 O 2 any halogen Alkyl Halides Br 2 moles HBr OH Br PBr 3 Pyridine Br Nu Nu Other Products Sn 2 BH 2 BH 3 OTs OMs Nu Nu OH MsCl Pyridine OMs OTf OH PCC O OH O O H O O 3 (CH 3 ) 2 SS N 1 reactions are therefore said to proceed with racemization If we start with a pure sample of (R)2bromobutane, for example, we expect the product of the S N 1 reaction with the OHion to be a racemic mixture of the two enantiomers of 2butanol We are now ready to address a pair of important questions
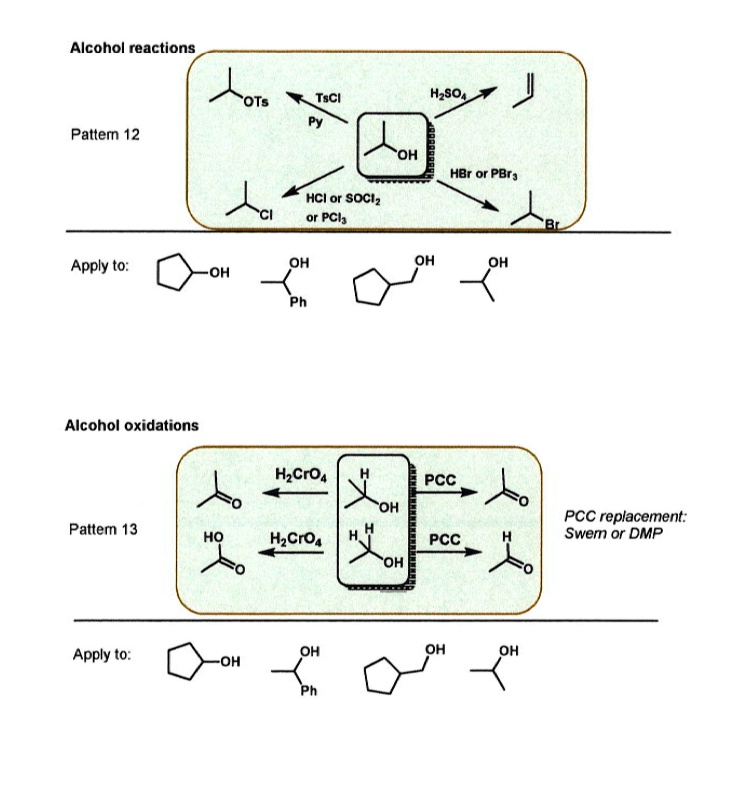



Solved Alcohol Reactions Ots Tscl Hzson Pattemn 12 Oh Hbr Or Pbr Hci Or Sociz Pcls Apply To Oh Oh Oh Oh Alcohol Oxidations Hzcroa Pcc Oh Pcc Replacement Swem Or Dmp Pattlem
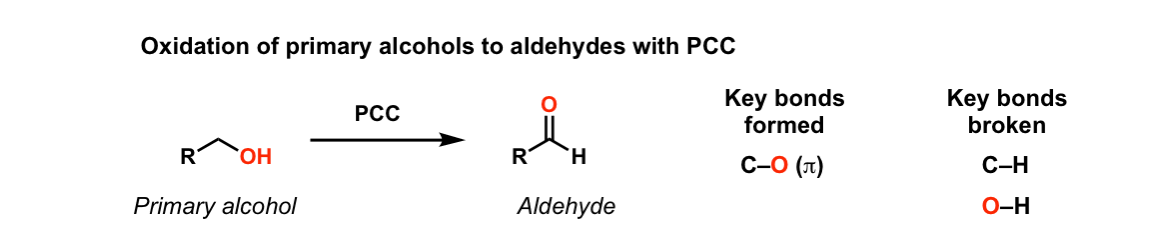



Oxidation Of Primary Alcohols To Aldehydes Using Pcc Master Organic Chemistry
3O Mn(OH) 2 (1730) CH 2Cl 2 (insoluble) (solvent) CH O (4methoxyphenyl)methanol (pmethoxybenzyl alcohol) 4methoxybenzaldehyde (81% yield) 179 Explain how and why the product(s) would differ in the following reactions of trans2buten1ol (1) Reaction with concentrated aqueous HBr (2) Conversion into the tosylate, then reaction with NaBrPyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC) CrO 3 6M HCl pyridine N H ClrO 3N H2 Cr 25 2PCC and PDC are soluble in anhydrous organic solvent such as CH 2Cl 2 The oxidation of primary alcohols with PCC or PDC in anhydrous CH 2Cl 2 stops at the aldehyde CH2Cl2 PCC OH CO2H CHO 1° alcohol H3O, acetone H2Cr2O7 Carboxylic Acid Aldehyde 333(PCC) Ch11 Reacns of Alcohols (landscape)docx Page 5 Alkyl halides can also be formed by reaction of alcohols with HX acids ROH HBr RBr H 2 O In acidic media, the alcohol is in equilibrium with its protonated form The –OH is a poor leaving group, but –OH 2
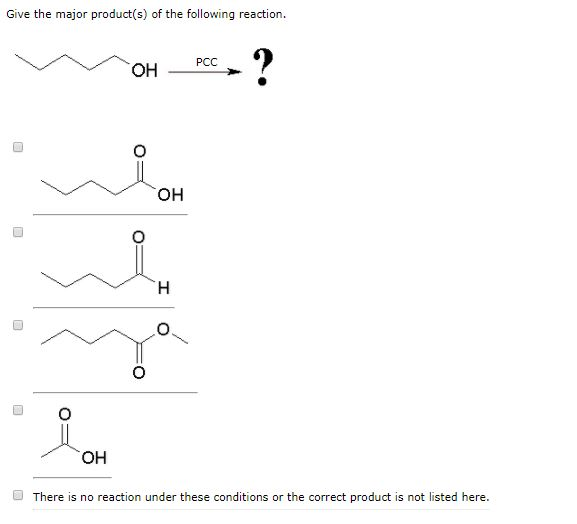



Solved Give The Major Product S Of The Following Reaction Chegg Com




Oxidation Organic Chemistry Jones Reagent And Pcc Youtube
Answer (1 of 2) CH3CH2CH2OH (1butanol) can be oxidised to CH3CH2CHO (butanal/butyraldehyde) by mild oxidising agents like pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC, yellow solid prepared by treating CrO3 with HCl in pyridine) or pyridinium dichromate ((PyH)2Cr2O7) or several other chromium based mild reagOH H • Note difference between • PCC and H 2CrO 4 when reacting with 1º alcohols Draw the products for the following oxidation reactions 1 PhOH PCC 2 PhOH H2CrO4 3 OH H2CrO4 4 OH OH PCC 5 OH OH H2CrO49 O O CrO 3 H 2 SO 4 Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 H 2 SO 4 OH PCC E Selfassessment Questions Can you write the reaction equations of alcohols reacting with active metals, such as Li, Na, and K?
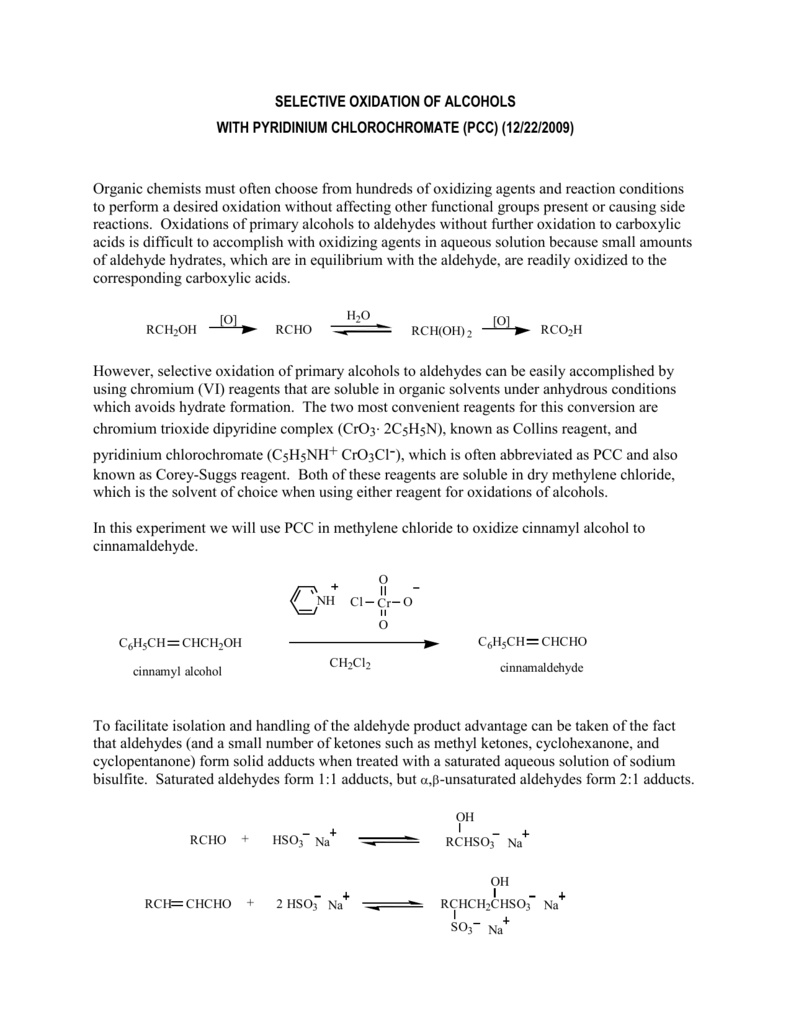



Selective Oxidation Of Alcohols With Pyridinium Chlorochromate




Orgo 2 Chapter 11 Flashcards Quizlet
The reaction of C H 2 = C H − C H 2 − O H with PCC takes place in the following manner C H 2 = C H − C H − O H → P C C C H 2 = C H − C H O (c) When phenol is treated with C H 3 C O C l /anhydrous A l C l 3 two products are formed among which one ofIf we use strong oxidizing agent such as H / KMnO 4 instead of PCC, we cannot prepare aldehyde from alcohol PCC Pyridinium chlorochromate Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yelloworange salt which is used to oxidize alcohols to carbonyl compounds (aldehyde and ketone) Ethanol and PCC reaction Ethanol and PCC react to give ethanal (aldehyde)Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Ph OH CH CH3 PCC (A) NH2 NH O C NH_2(B) Product B in the given reaction is




Pyridinium Chlorochromate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Alcohol Reactions Of Alcohols Britannica
Pyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC) Oxidation This is a Cr 6 salt formed between pyridine (C 6 H 5 N), HCl, and CrO 3 It is soluble in halogenated organic solvents such as dichloromethane which allows carrying out the reaction in the absence of waterExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 100% (6 ratings) Transcribed image text Predict the product for the following reaction OH CH2OH PCC excess CH2Cl2 OH OH OH Me^o J CH2Cl2, 1 h, 40 °C OH Ref 271 PCC cleaves the furan ring, giving a conjugated endione The unreacted alcohol attacks one of the ketones, yielding a cyclic hemiacetal 1524 Tertiary Allylic Alcohols PCC reacts with tertiary allylic alcohols, forming an intermediate chromate ester that evolves giving a conjugated enone or enal



Organic Chemistry On Line



Pyridinium Dichromate Pdc
PCC was invented as a workaround to this problem it works as a reactant in anhydrous enviroment, hence stopping the reaction at the aldheyde stage An alternative way to see PCC is to follow its preparation if you add C r O X 3, H C l and pyridine, PCC is formed If you add C r O X 3, acid and water, chromic acid is formed



Oxidation Of Alcohols Examples Video Khan Academy




Alcohol Oxidation Mechanisms And Practice Problems Chemistry Steps




Can Methanol Be Oxidised By Pcc Chemistry Stack Exchange



1




Pcc Reagent Definition Preparation Reaction Mechanism




Pcc Pdc Oxidation Chem Station Int Ed




Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc



Solved Oh Pcc Oh Oh Och3 Oh Oh A Och3 B Oh Oh Oh Oh Och Och D C Course Hero




Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc Oxidation Of Alcohols




Oxidation To Ketones Pcc Others Chemistryscore




Chapter 11 Reaction Of Alcohols Pdc Or Pcc H Ox H C C Oh Biewerm 2325 Cent Nbsp Conversion Of Alcohols Pdf Document




Organic Chemistry Oxidation Jones Reagent And Pcc




Alcohol Reactions Conversions To Esters Acetate Lab Reactions With Hydrogen Halides Acid Catalyzed Hydrations Ppt Download




Pdf Selective Oxidation Of Secondary Over Primary Hydroxyl Group




Using Pcc Organic Chemistry
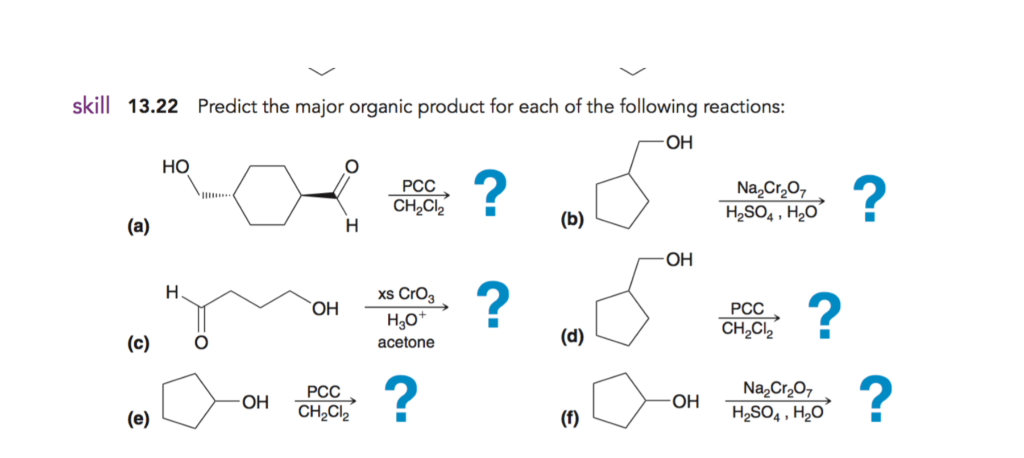



Solved Skill 13 22 Predict The Major Organic Product For Chegg Com




Predict The Product For The Following Reaction Oh Pcc Ch C12 Predict The Product For The Following Homeworklib




Recent Advances In Application Of Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc In Organic Synthesis Bentham Science



What Is The Oxidation Of Active Methylene Compounds By Pcc With Mechanism Quora




Pyridinium Chlorochromate Wikipedia




50 Consider The Following Reactions Oh Pcc Phcho B Major Ch Ci Dil Naoh Major Product



Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc




Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc Oxidation Of Alcohols
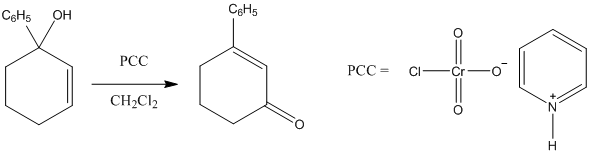



Solved The Tertiary Alcohol Below Was Reacted With Pcc In Ch2cl2 Chegg Com




What Is The Product When But 2 En 1 Ol Gets Oxidised By Pcc Organic Chemistry Doubts Goiit Com




Pyridinium Chlorochromate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Reagent Friday Pcc Pyridinium Chlorochromate




Lu Nisu3 Oh Oh Loh Oh Pcc Excess A 1 Equivalent B H Chzmgbr C Nabh4 D H30 Product D Will Be Oh Oh Oh Ch Ch3 Ch Ch3 O Y Oh 0



Oxidation With Chromium Vi Amine Complexes Organic Reactions Wiki




Solved Reaction Of The Following Compound With Pcc Gives Product With Functional Groups Of Oh Pcc Ho Oh Select One A Three Ketones B 30 Alcohol And Two Ketones C 30 Alcohol And




07 11 Weak Oxidations And Pyridinium Chlorochromate Youtube




Using Pcc Organic Chemistry




Pyridinium Chlorochromate Wikipedia



Solved 10 What Would Be The Major Product Of The Following Reaction Sequence Oh Pcc I Lda Ch C12 Ii Chi I Ii Iii Iv 4 A B 1 H Ii



2




Weak C O Bond Oxidations With Pcc Dmp Etc Youtube
.jpg)



Oxidation Of Propanol Ch3ch2ch2oh With Pcc And Kmno4
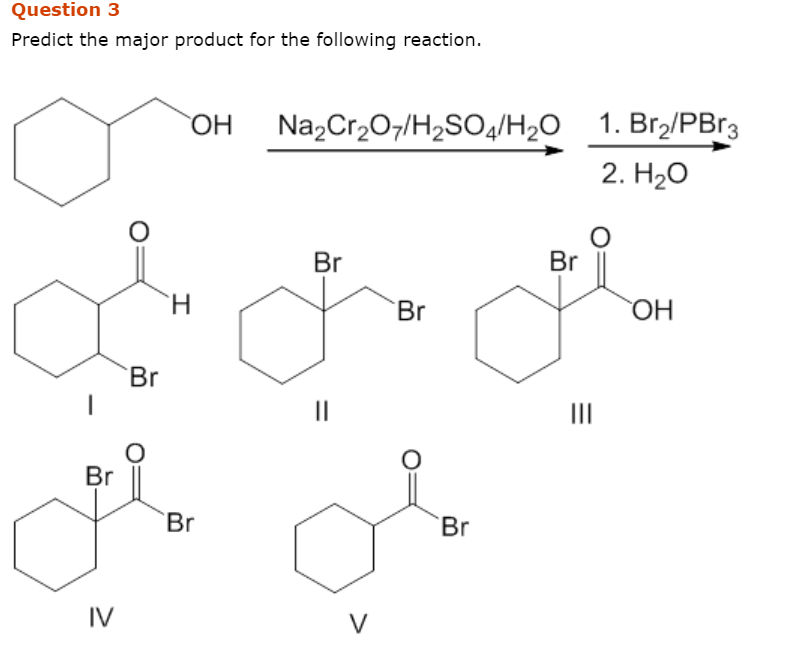



Solved Predict The Major Product For The Following Reaction Chegg Com




Using Pcc Organic Chemistry



Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc



1
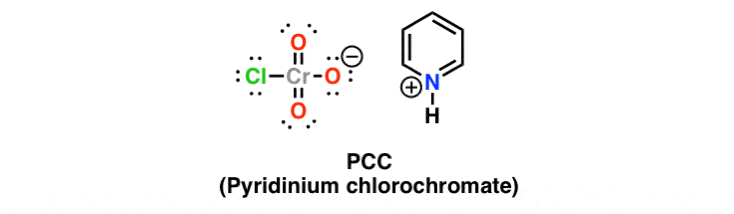



Reagent Friday Pcc Pyridinium Chlorochromate




Oneclass Oh H2so4 Acetone Ho Oh Oh Pcc 2 Equiv H Oh Pcc 2 Equiv Ch2cl2




Write Thereactions Product S In Thefollowingohcooh Ch Co H Gt Pcc Ii Ch3 Ch Ch Ch2 Oh Gt 2 5 Brainly In




Pcc Reagent Definition Preparation Reaction Mechanism




15 6 Reactions Of Alcohols A Review And A Preview Copyright C The Mcgraw Hill Companies Inc Permission Required For Reproduction Or Display Ppt Download



Give The Product Expected When The Following Alcohol Reacts With Pyridinium Chlorochromate Pcc Assume That Pcc Is Present In Excess
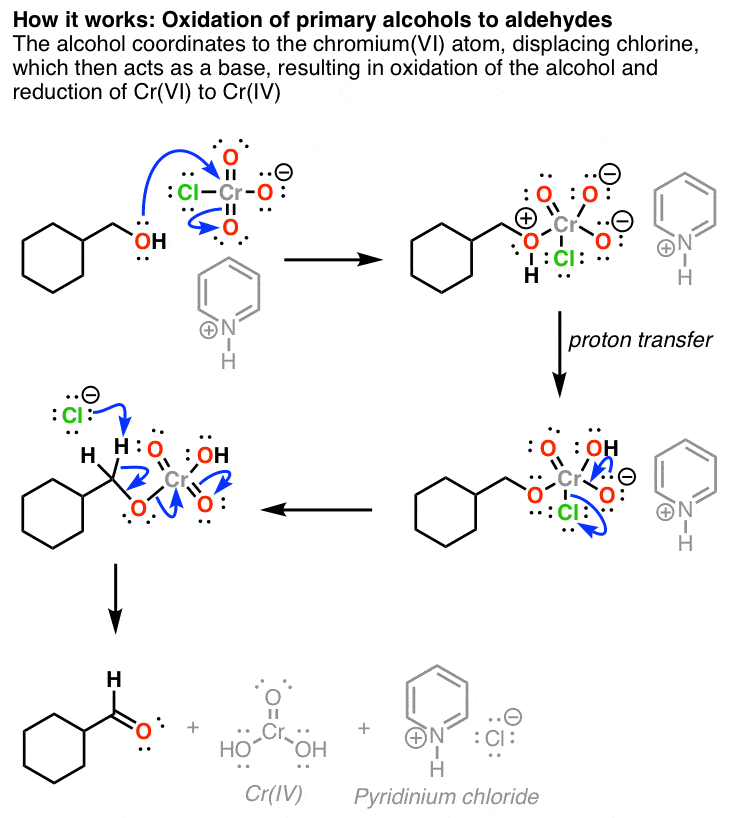



Reagent Friday Pcc Pyridinium Chlorochromate
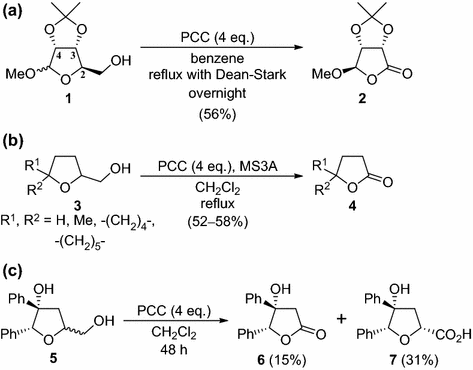



Practical And Environmentally Friendly Transformation Of Tetrahydrofuran 2 Methanols To G Lactones Via Oxidative Cleavage Springerlink



Alcohol Reactivity



Oxidation By Pcc Pyridinium Chlorochromate Chemistry Libretexts




Pcc Chemistry Reagent Chemistryscore




Oxidation Of Alcohols Pcc Pdc Cro3 Dmp Swern Practice Problems Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Organic Chemistry




Select More Than One Steps Oh Pcc Nabha Ch3oh 1 Mgbr Ch2cl2 Etoh H 2 H Homeworklib




Give The Product Expected When The Followi Clutch Prep




Oneclass Give The Major Product S Of The Following Reaction Pcc Oh Oh There Is No Reaction Under T
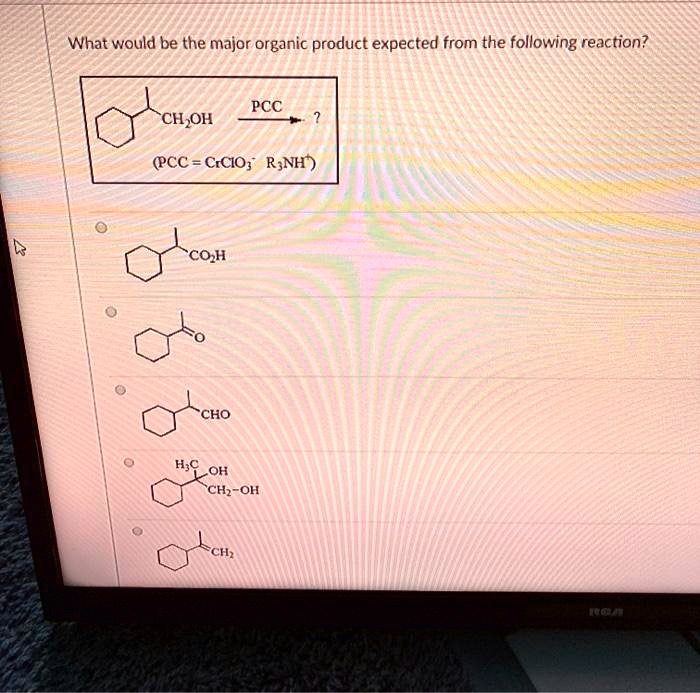



Solved What Would Be The Major Organic Product Expected From The Following Reaction Pcc Ch Oh Pcc Ccio R Nh Coh Cho H E Oh Chz Oh




Pcc Oxidation Mechanism Chemistry Steps



Alcohol Oxidation Mechanism With H2cro4 Pcc And Kmno4 Youtube



Ochem




Schematic Diagram Of Carbonation Process For Scalenohedral Pcc Download Scientific Diagram



Chapter 8 Pages 31 And 32




Alcohol Reactivity




Pcc Reagent Definition Preparation Reaction Mechanism
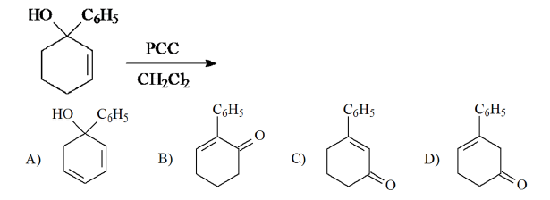



Solved The Tertiary Alcohol Below Was Reacted With Pcc In Ch2cl2 Chegg Com




Pcc Reagent Definition Preparation Reaction Mechanism




Using Pcc Organic Chemistry




Give The Product Expected When The Followi Clutch Prep
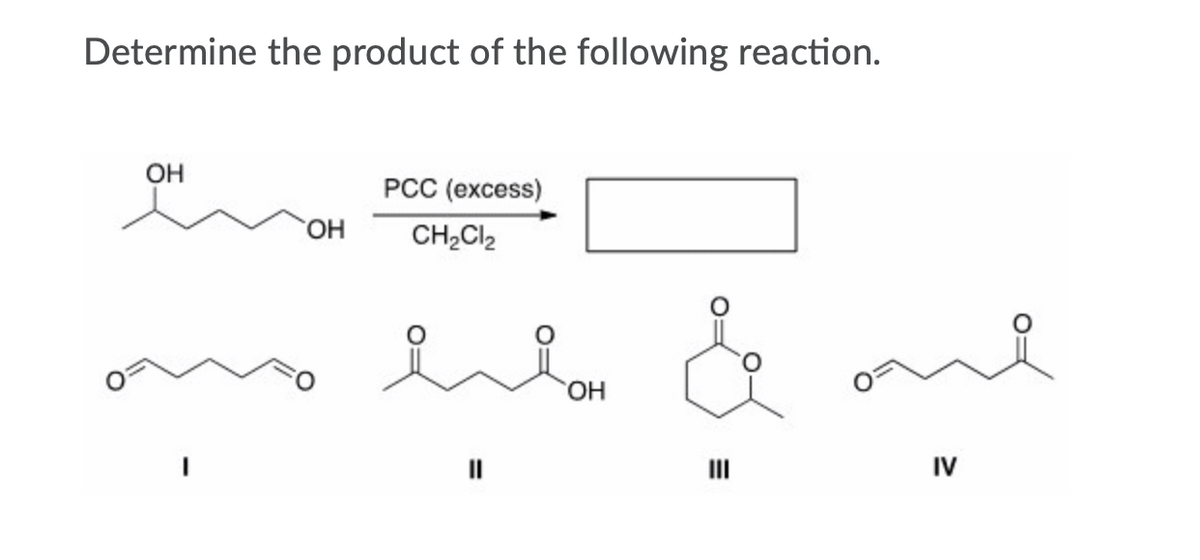



Answered Determine The Product Of The Following Bartleby




Why Can T We Oxidise Allylic Alcohol To Aldehyde Using Pyridinium Chlorochromate Chemistry Stack Exchange
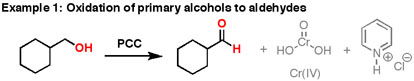



17 7 Oxidation Of Alcohols Chemistry Libretexts



Pyridinium Chlorochromate Ochempal




Xrd Peaks And Sem Photographs Of Pcc Synthesized From Reaction 3 Download Scientific Diagram
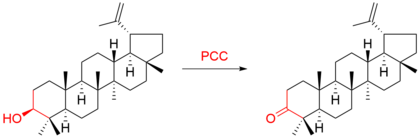



Pyridinium Chlorochromate Wikipedia




Can I Use Pcc Or Cro3 For In Any Of The Two Reactions Interchange Or Is Pcc Specific For The Given Reaction R Chemistry




Pcc Mediated Novel Oxidation Reactions Of Homobenzylic And Homoallylic Alcohols Sciencedirect



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿